Table Of Content
The Spitfire, however, ignored both refinements and used a voluminous wing-root fairing, a solution that simplified wing construction but might have cost a smidgen of speed or climb rate. Indeed, the virtues of elliptical wings had been articulated by British theorist Frederick Lanchester in 1907. The shape had been chosen for the Spitfire “early on,” Shenstone said, because Mitchell, having used thick airfoil sections on a lackluster precursor of the Spitfire, wanted thinner ones for the new fighter. The problem was that the four .303 machine guns per side required by the Royal Air Force would not fit within a thin wing of straight taper. The elliptical wing’s taper began fairly far outboard, and so it enveloped the guns comfortably. “I don’t give a damn whether it’s elliptical or not so long as it covers the guns!
New Report: Engine Problems Led to MQ-9 Crash in Africa Last Year
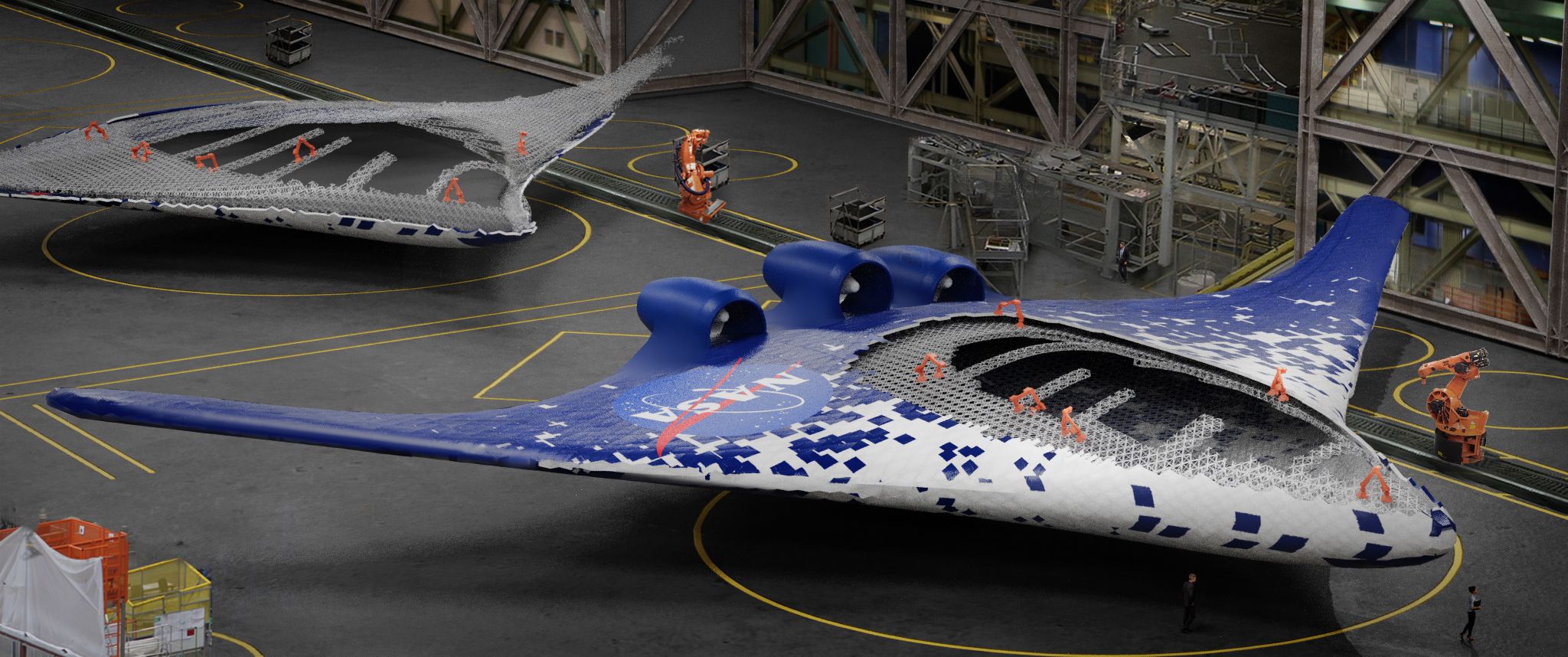
Air Force selects JetZero for blended-wing body prototype plane - Defense One
Air Force selects JetZero for blended-wing body prototype plane.
Posted: Wed, 16 Aug 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Among these components, aircraft wings stand out as a clear sign of the ingenuity of aeronautical engineering. It is a non-tapered, straight wing that is mostly used in small aircrafts. This wing extends out from the aircraft’s fuselage at right angles (approximately). Aircraft wings may be attached at the bottom of the fuselage, mid-fuselage or at the top. They might extend perpendicular to the fuselage’s horizontal plain or can angle down or up slightly.
Return of the Flying Wing
In order to efficiently analyse the wing structure, a number of simplifying assumptions are typically made when working with a semi-monocoque structure. While we all wish we had unlimited funds and that price was no factor in our choice of personal aircraft, the reality is that most would-be aircraft owners must stick within a certain budget when choosing their next plane. We are excited to share with you an updated version of our 2024 guide to affordable personal aircraft.
NASA’s Near Space Network Enables PACE Climate Mission to ‘Phone Home’
A revolutionary plane coming soon – UCI News - UCI News
A revolutionary plane coming soon – UCI News.
Posted: Mon, 30 Oct 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
The wing has a central hinge which, when rotated, sweeps one end of the wing forward while pushing the other end back. Many commercial aircraft have swept wings due to the fact that they reduce turbulence. A tapered wing promotes low drag as well as superior durability during rapid air travel, so it was a popular choice in the early days of supersonic aircraft technology. This aerodynamic approach provided impressive performance and was implemented by several aircraft models. There is something that unifies all pilots together—an unwavering fascination with the wonder of flight and the multiple components that make everything possible.
This is the case with fighter jets, racing airplanes, and aerobatic aircraft. These airplane wings are shaped differently than those used for training or passenger and cargo transportation. Although the airplane is comparatively more difficult to control, its maneuverability and possibilities involving lift are increased. This enables the pilot to perform barrel rolls, impressive banks, rapid acceleration, and even loops. Admit it — there are things you don’t know, but should know, about aircraft wings.
Ogive wing designs provide top performance and supersonic speeds while minimizing drag. In this article, we will explore the diverse types of aircraft wings, delving into ten distinct designs that have left their mark on the history of aviation. Swept wings are mostly suitable for high speeds, like supersonic and transonic, while unswept wings work best for low speeds i.e. subsonic. Variable sweep wings were designed to optimize flight experience over a range of speeds.
Sweepback on the wing, which is used to delay the onset of compressibility effects, can also introduce certain undesirable flight dynamic characteristics, which can be offset using anhedral. The total drag is simply the summation of the two drag components and based on the formulae will present a minimum drag at a particular speed. It makes sense to design your aircraft to cruise at or near the minimum drag point and varying aspect ratio is one way to do so. It is worth mentioning that at this point another trade-off exists between minimising drag at cruise and providing enough wing area to allow the aircraft to takeoff and land safely. Zero-lift drag (often also called parasitic drag) is the drag that exists as a consequence of moving a body through a medium.
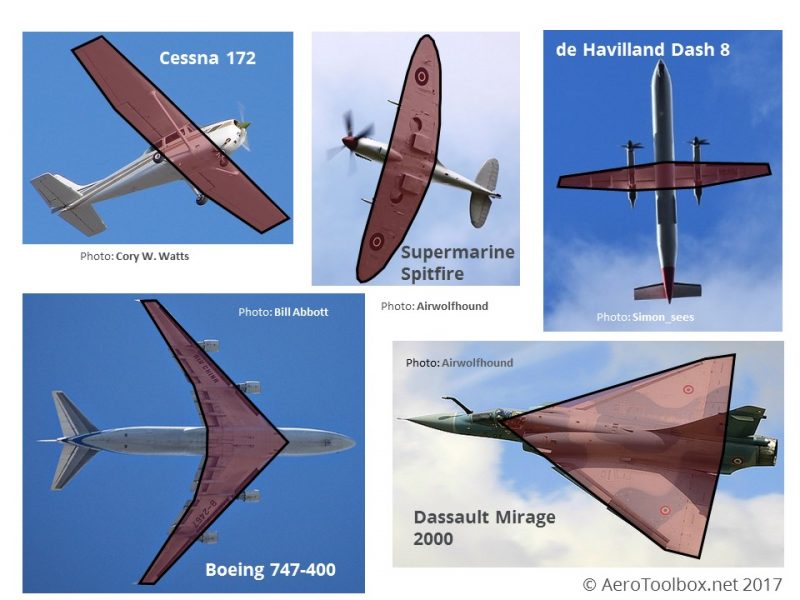
High wing aircraft have their wings mounted to the upper surface of their fuselage, or on top of it. For multi-engined aircraft, high wings enable the fuselage to be closer to the ground, which is ideal for large cargo planes and military transports. For reference, control surfaces are portions of an airplane that are involved in steering. Mid wing airplanes are very maneuverable, but not as stable as high wing airplanes. As the name suggests, a low wing configuration is one where the wings are mounted below the midline of the aircraft. By placing the wings in this configuration, the pilot can benefit from improved visibility, and it also frees up space in the fuselage from the wing spar carry-through needed for higher mountings.
An aircraft does not just fly straight and level during all phases of operation. In this instance, the wing is producing a lift force equal to twice the weight of the aircraft and the aircraft is said to be pulling 2g’s (twice the gravitational force) or operating at a load factor of 2. The last three posts in this series have focused on the conceptual design of the wing. We examined wing area and aspect ratio, introduced sweep and drag divergence and looked in more detail how the airfoil profile determines the flying characteristics of the aircraft.
Four fixed vertical fins were mounted on the trailing edges for stability and four shallow “fences” or air dams ran from front to back to help channel the airflow. Northrop disliked the intruding fins but they added, in their way, to the sleek appearance of the aircraft. There are a lot of new drawings, and the drawings previously on this websitehave been processed and cleaned up.
The principle identified by Lanchester is that induced drag is at a minimum when the spanwise distribution of lift is elliptical, and there is an equation to prove it. Wing ribs are spaced along the span of the wing and give the wing its aerodynamic shape. The ribs, spar caps, and stiffeners form bays throughout the wing that support the wing skins against buckling. Any point loads introduced into the wing are done so at ribs which form hardpoints.
Actual aircraft wings are complex three-dimensional objects, but we will start with some simple definitions. This airfoil is a modern, thick airfoil, which is slightly different from the thin airfoils used by the Wrights and shown below. The ratio of the length of a wing to its breadth is known as aspect ratio. It was understood even in the 19th century, from observations of birds, that wings of larger span and higher aspect ratio could carry a load with less effort (because their induced drag is less). On the other hand, such wings on airplanes, as opposed to birds, are less maneuverable in flight and more difficult to make strong and stiff than short, broad ones of lower aspect ratio. He started with a conventional wing design and, relying on intuition, used auto body putty to add bulk to some areas while filing away others, testing and retesting his models in Langley’s high-speed wind tunnel.

No comments:
Post a Comment